The mechanisms leading to erosion of sediment particles in turbulent flows
- Ansprechperson:
- Projektgruppe:
- Förderung:
Analysis of turbulence-induced sediment erosion and near-bed transport is vital to many aspects of hydraulic engineering including the design of stable channels, protection of bridge piers, and the development and management of aquatic habitats. Most currently available relations for predicting sediment erosion thresholds and bed-load transport rates are empirical and employ time- and space-averaged bulk quantities. In the present project we are investigating the fundamental mechanisms of sediment erosion by means of direct numerical simulation involving fixed as well as freely mobile particles.
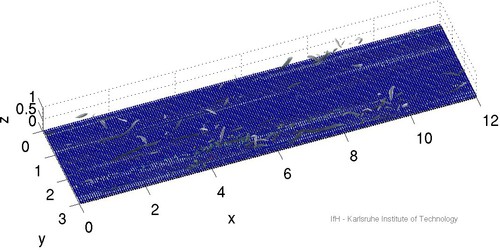
[1] C. Chan-Braun, M. Garcia-Villalba, and M. Uhlmann. Force and torque acting on particles in a transitionally rough open channel flow. J. Fluid Mech., 684:441-474, 2011, [DOI]
[2] C. Chan-Braun, M.García-Villalba, and M. Uhlmann, Spatial and temporal scales of force and torque acting on wall-mounted spherical particles in open channel flow. Phys. Fluids, 25(7):075103, 2013, [DOI]